Everyone uses Google to conduct online searches, but there are a few search operators that can be incredibly helpful for entrepreneurs. Use these simple Google search operators to boost your business’s exposure online.
Find Specific Document Types
The filetype operator helps you search for documents of a certain file type. Simply place the desired keyword or phrase in front of the operator, and Google will only return results that match the specified file format.
Syntax: “keyword(s)” filetype:extension
The extension can be anything you need: doc, pdf, xls, ppt, and so on.
Example: “self-publishing tips” filetype:pdf
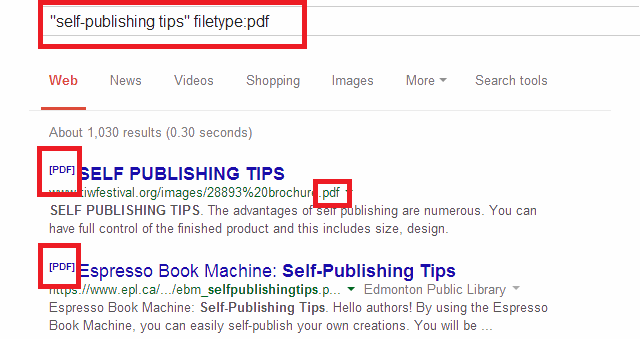
How can the filetype operator help your business?
Businesses can promote themselves effectively by producing helpful reports and e-books that address their customers’ problems. These reports and e-books can then be distributed through various websites and online file upload sites like SlideShare, Scribd, and so on.
Often, the download links to these reports can also be sent to niche-specific influencers through social media and email. If your reports are exceptionally good, they may choose to share them with their blog readers, fans, and followers, significantly boosting your website’s exposure.
When people download your e-book or report, they should get the information they were looking for; however, the report should entice the reader to click your website link for more information, a free trial, or further assistance.
When properly written, a free e-book or report helps build your online business’s niche credibility and quickly establishes you as an authority in your industry.
Since most online niches are highly competitive, you need all the help you can get. By creating high-quality, niche-related e-books and guides, you will rise above your competition.
These reports help you engage your customers and directly convey your message. You will have their undivided attention while they are reading the e-book.
Power Tip: Make a list of your top competitors’ reports. Use the filetype Google search operator to find authoritative websites that have published those reports, and then contact their webmasters, asking them to publish your free reports as well.
Use Explicit Phrases
Surrounding a word or a group of words with quotation marks helps you find explicit mentions of the word(s).
Syntax: “keyword(s)”
Example: “self-publishing guide”
The Google search in the example above will return pages that explicitly contain the “self-publishing guide” group of words in their title or article body.
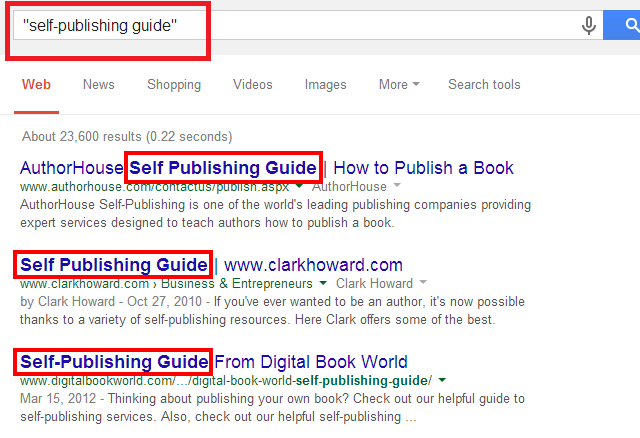
How does this operator help entrepreneurs?
You work hard to get your online business noticed. You have probably written some high-quality articles to spread the word about your business.
You might have established social media accounts on top sites, engaging your site visitors and potential audience members.
You might have contacted other websites in your niche, asking them to publish your outstanding articles or content that mentions and links back to your website.
You might have sent out many targeted press releases.
All your promotional efforts might have resulted in a few backlinks and website visits. However, some of the mentions your brand has gotten online are not linking back to your website.
This is a wasted website traffic opportunity.
You can use the explicit phrase Google search operator to reclaim all mentions of your brand online.
Whether people are talking about your brand in a blog post or on a forum, when you use this search operator, you will find the mention. Then, you can ask the bloggers who have mentioned your company to also include a link to your site.
This helps your website get better rankings and receive more targeted visitors, boosting your online business’s profits.
It is important to understand that search engines rank your site based on the quality and quantity of backlinks. Use the explicit phrase search operator to turn those brand mentions into backlinks to your website, so you can get more website traffic from search engines.
Since people are already mentioning your brand, you should make these mentions work for you by reclaiming them and turning them into live links.
Perform Site-Specific Searches
This operator searches a particular website for content that mentions a specific word or group of words.
Syntax: “keyword(s)” site:domain
Example: “guest post” site:copyblogger.com
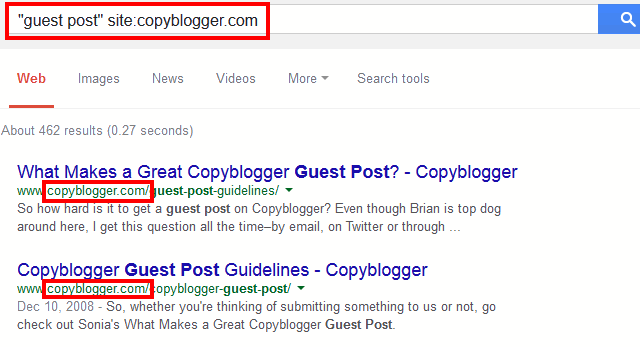
Why use this?
One of the most effective ways to get search engine traffic for your online business is through guest posts on authoritative sites in your niche.
While it is fairly easy to compile a list of websites that are respected and/or authoritative in your niche, it can be harder to find out if they are interested in guest posts from outside content creators.
The site: Google search operator will help you determine if a particular website is interested in guest posts, for example.
This operator will also help you identify if that particular website has already covered specific topics; you want to focus your energy on creating 100% unique content. It’s a simple method that increases your chances of getting your guest post accepted and published.
Get Creative with the Wildcard Operator
This operator helps you find content that includes the specified keyword(s) and other words or phrases. The wildcard operator, represented by an asterisk (*), helps you find content that is related to your keyword(s).
Syntax: keyword(s) * keyword(s)
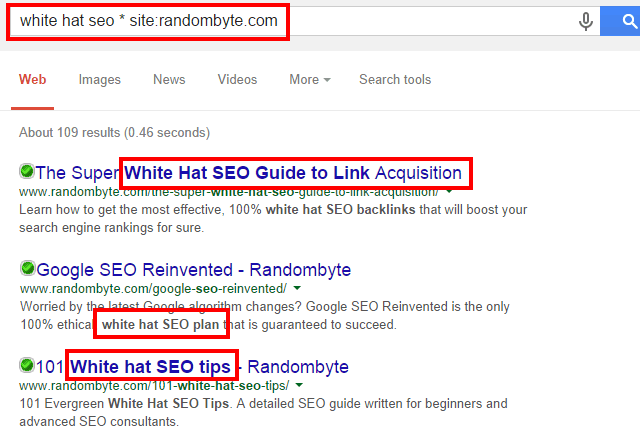
Example: small business * report
In this case, the wildcard operator symbol will be replaced with various words or groups of words. For laser-targeted results, combine the wildcard and the explicit phrases (quotes) operators.
Example: “small business * report”
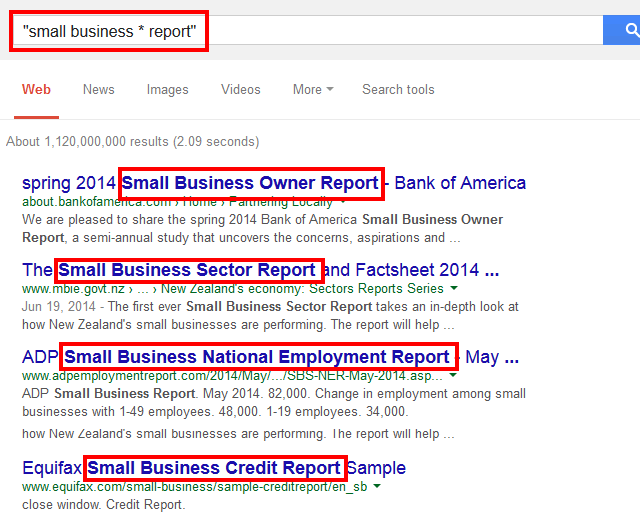
But how can this Google search operator help?
This command allows you to generate various ideas for your own reports and even discover new product ideas.
It also helps you discover your competitors’ top web pages that address a particular topic. Analyze each page, take note of their great ideas, and then create even better content pieces that provide more value to the reader.
Search Results Exclusions
This operator prevents pages containing specified excluded words from showing up in Google’s search results. It allows you to find content that includes your target keywords or phrases but excludes unwanted keywords or phrases.
Syntax: keyword(s) –unwanted word(s)
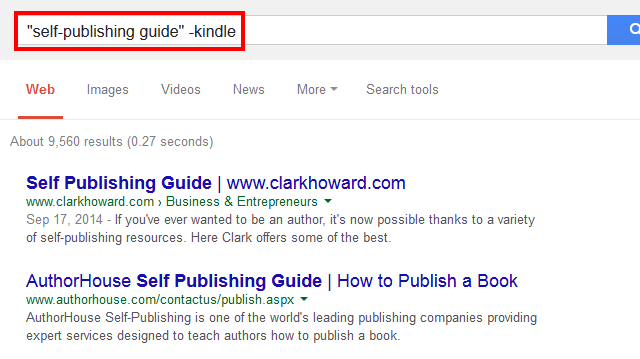
Let us pretend that you plan to write and publish a book but aren’t interested in publishing for Kindle. You would use a search string like the one below:
Example: “self-publishing guide” –kindle
The example above shows how easy it is to exclude a specific brand, product, or service from the search results pages. Use this search operator to determine which national or international suppliers haven’t signed contracts with your local competitors. Then, get in touch with them and become their reseller.
If your competitor’s name is Kemykals, Inc., and you are a paint importer, you would use a search string like this:
Example: “paint suppliers” -kemykals
The Cached Content Operator
This operator helps you view unavailable content using Google’s caching technology. It is a well-known fact that many sites ‘disappear’ for days, weeks, or even months due to domain or hosting fee non-payments, legal issues, and a wide variety of other problems.
Often, the website you are interested in is temporarily offline, but you need to access its content immediately. The good news is that Google’s cache operator makes this possible.
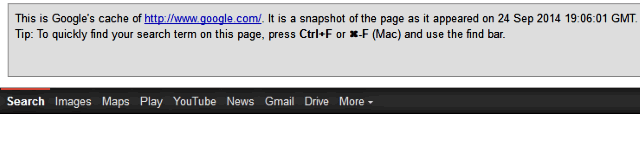
Syntax: cache:domain
Example: cache:google.com
List Your Business on Wikipedia
This combination of operators finds pages on Wikipedia with citations that link to a dead URL.
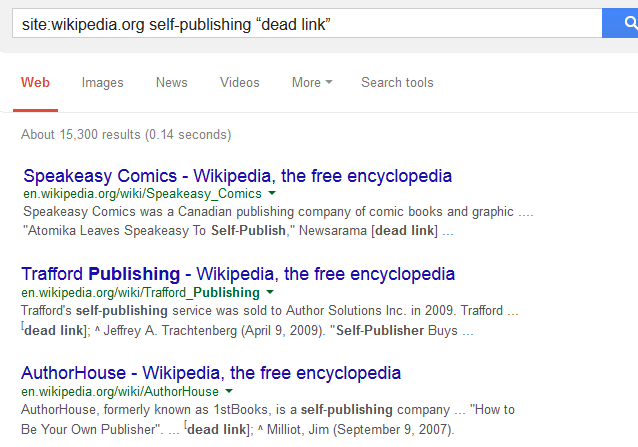
Syntax: site:wikipedia.org keyword(s) “dead link”
Example: site:wikipedia.org self-publishing “dead link”
Explore Google’s search results, find a relevant, niche-related dead link on the page, and then create a fantastic resource page that can serve as a replacement for the dead link.
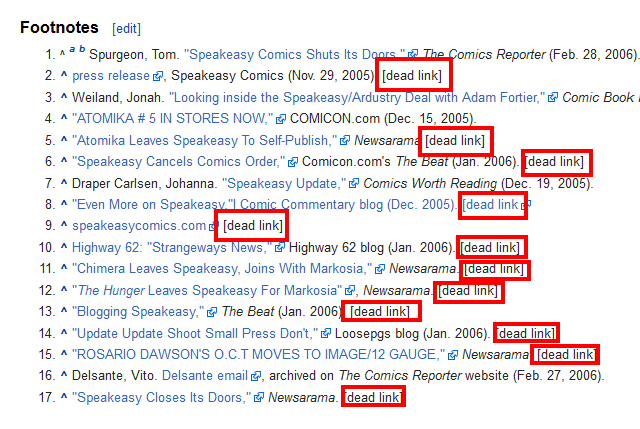
Use WayBackMachine to see an actual copy of the dead resource page, and then update and improve it. Add more content, videos, infographics, etc., to make it better.
Resist the temptation to simply copy/paste the content of the dead resource onto your website; this may get you into trouble.
Don’t forget that your resource shouldn’t be promotional at all. If it adds value to the Wikipedia page, you can add its link to the target page using a free Wikipedia account, and it will stick.
Bonus Tip for SEOs: Input the dead link URL into a backlinks discovery tool, and then notify the webmasters who were linking to it that the old resource is dead. Suggest your great resource page as the perfect replacement. It’s a quick and effective way of getting niche-related, powerful backlinks.
Remove Results from Specific Domains
This minus (-) operator removes results from a specific website.
Syntax: keyword(s) -domain
Example: kindle -amazon.com
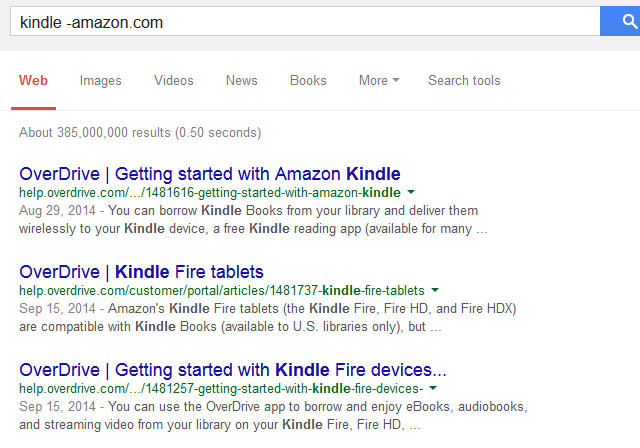
Why use the search exclusion operator?
First, you want to keep an eye on your competitors. What are people saying about them? How often do they send out press releases?
A Google search like the one below will reveal all your competitor’s brand mentions, excluding those from their own site.
Example: kemykals –kemykals.com
Here’s another idea: if you are doing research for your blog posts, reports, and so on, the last thing you want to do is waste your time manually filtering results from low-quality sites with tons of junk pages.
If you know that a particular website publishes useless, low-quality articles, you can exclude it from the search results pages right off the bat.
Find Highly Targeted Web Pages
This allintitle operator returns webpage pages that include all the specified keywords in their titles.
Syntax: allintitle:keyword(s)
Example: allintitle:self-publishing tips
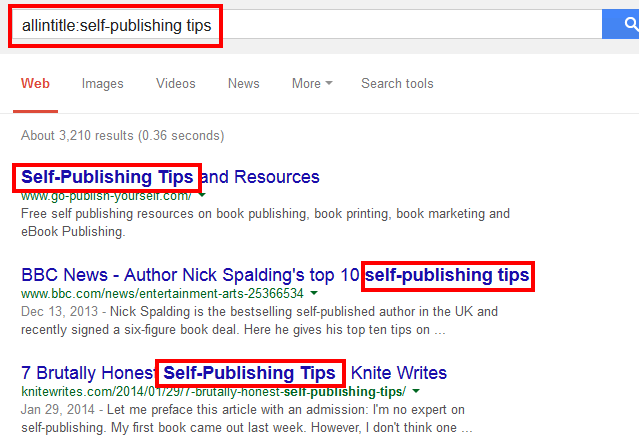
How to use the allintitle operator?
The web is constantly growing, and this means that the number of search results is also growing each day. How can business owners keep up with the latest industry news when they have to go through tens or hundreds of search results to find the good stuff?
Fortunately, allintitle allows you to find highly relevant resources. If a blogger has taken the time to name their page “Self-Publishing Tips and Resources,” that page should contain self-publishing tips and resources, right?
You are probably running a business in an industry where people maintain niche-specific directories, which are extremely valuable because they can send qualified website traffic. Here is an example to find directories in the self-publishing niche:
Example: allintitle:self publishing directory
Discover Related Websites
The related operator helps you find websites related to the specified domain.
Syntax: related:www.domain.com
Example: related:www.cnn.com
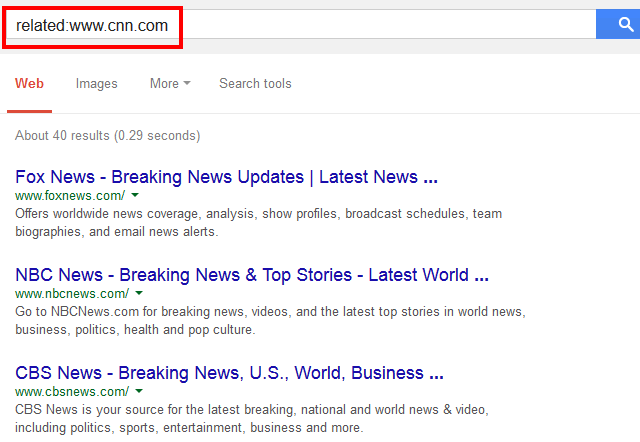
How to use this search operator?
If you have a tough time finding industry-related websites for partnerships, outreach, and backlink building purposes, this search operator will help you tap into Google’s ability to discover related sites.
Use this operator to find websites in the same niche or content category, starting with a website you already know is relevant.
Basically, you only need to start with one ‘seed’ website. The “related” search operator will help you discover dozens of similar sites. Then, use the operator again with each newly discovered site, and you will quickly end up with a list of hundreds of industry-related websites.
Use these related sites to boost website traffic and build backlinks. Contact their owners, asking them if they are interested in posting your high-quality content or interviewing them on your blog.
When you interview site owners, they will often link back to your website or at least mention the interview URL on Twitter/X or other social media platforms.
These are the most important Google search operators that can boost your business’s profitability. Use them creatively, and you will quickly be able to learn from and then dominate your competitors.

