Everyone loves a quick SEO win! This is one of the most comprehensive collections of search engine optimization tips on the Internet, and it is constantly growing. So, make sure to bookmark the article and share it with your friends.
The tips are split into categories; use the links below to jump to a specific category, or scroll down the page to read them all in order.
167 Evergreen White Hat SEO Tips
Table of Contents
Part 1: Site Design & Architecture
Part 6: Off-page SEO / Link Building Tips
Part 11: Google Penalties and Recovery
Part 12: General SEO Tips and Advice
Part 1: Site Design & Architecture
1. Plan your site structure before starting to build it. Ensure that the content is logically organized, allowing the use of targeted keywords for relevant categories.
2. Create dedicated pages for each targeted keyword, but avoid overdoing it. For instance, if you target the keyword “business branding ideas,” create a page like this for your site:
https://www.yoursite.com/business-branding-ideas
Resist the temptation to create additional pages for similar keywords like “small business SEO tips.” Following a good SEO strategy will allow a single page to rank for several related keywords. Having multiple similar pages could attract a Google Panda penalty.
3. If launching a new site, consider using the table of contents (TOC) of a popular book in your niche for your website’s categories.
For example, the TOC of a vegetarian cookbook can help design a site for vegetarian content.

4. Ensure no page on your site is more than 2-3 clicks away from the homepage. This keeps the link juice flowing properly and avoids pages ending up in Google’s supplemental index.
5. Check and fix your website’s HTML and CSS. Minor errors won’t get your site penalized, but excessive errors can affect crawling. Use a free validator like https://www.onlinewebcheck.com/
6. Consider using WordPress for new sites; it’s fast, easy to use, and has many free SEO-related plugins.
7. Keep important content above the fold. Avoid placing ads above the fold, as Google dislikes this and it can lower your rankings.
8. Ensure the “title” and “description” tags include the targeted keyword as close to the beginning as possible. Include the keyword in the URL as well. For example, you can target the keyword “seo tips videos” using a URL like this:
https://www.yoursite.com/seo-tips-videos
9. Have a dedicated “Contact Us” page with your business address. This assures Google of the legitimacy of your business.
10. Meta keywords are ignored by Google but still useful for less popular search engines. Use a few relevant keywords for this meta tag.
11. Link to other articles/pages on your site whenever possible to keep visitors longer and boost rankings.
12. Add a blog and regularly post high-quality content targeting long-tail keywords to attract more visitors.
13. Create an XML sitemap and submit it using Google’s Search Console to ensure faster crawling and indexing. Use https://www.xml-sitemaps.com/
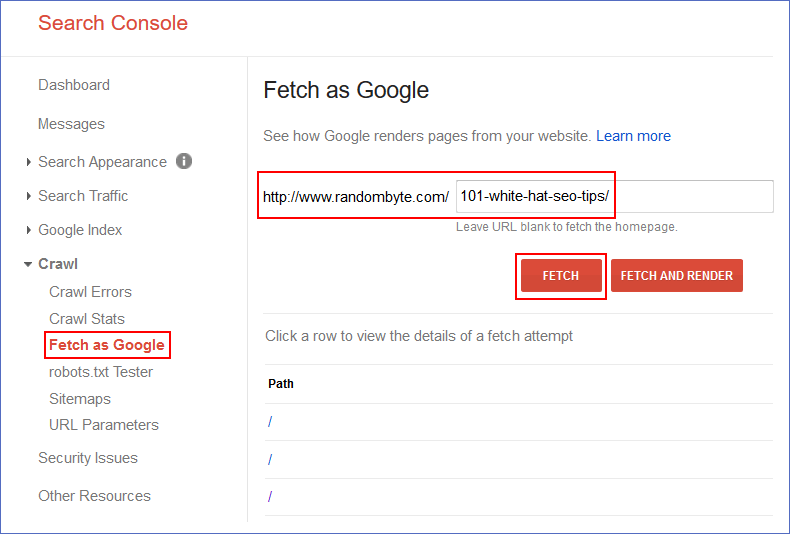
14. Use Google Search Console’s “Crawl” -> “Fetch as Google” to evaluate your site’s mobile/desktop compatibility.
15. Google’s Exact Match Domain update has devalued keyword-inclusive domains. However, buying an aged domain is still beneficial.
16. Thoroughly check aged domains before purchasing, ensuring they have many links from reputable sources.
17. Avoid penalized domains. Google the URL and check if it ranks #1 for its own name; if not, it might be penalized.
Avoid buying any domain, no matter how great it may look, if it has even a few shady backlinks pointing to it.
18. Choose .com domains for general use, and .org for non-profits. Avoid hyphenated domains as they often rank poorly.
19. Minimize page sizes by optimizing images and code to improve loading speed, a significant ranking factor. Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool for guidance.
20. Ensure images are properly optimized. Limit image width to 1000 pixels to save server space and improve site load time on mobile devices.
21. If you’ve bought a great domain but you’re not ready to launch a new site, put up a high-quality article on the homepage and get it indexed to help the site age naturally.
Part 2: Keyword Research
22. Use tools like Ubersuggest to discover less-known keywords.
23. Discover unique keywords from sites like Wikipedia, Quora, and Reddit. Go to each site, type in the keywords that interest you in the search box and then pick the most relevant results.
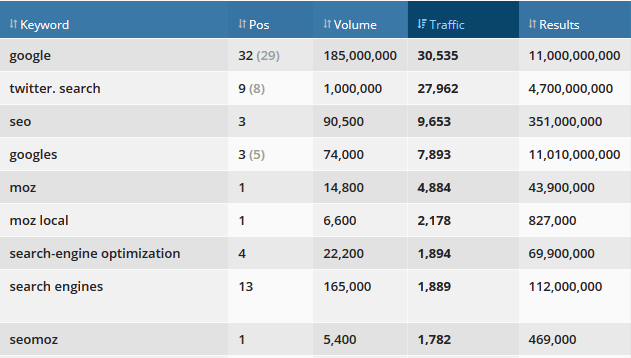
24. Extract competitors’ keywords using tools like SEMrush, Spyfu, and Ahrefs.
25. Verify new keywords’ profitability by testing them with a small Google Ads campaign. Use conversion tracking, let the campaign run for a few weeks and then evaluate the results.
26. Use third-party tools to find profitable keywords for SEO campaigns by noting the high CPC keywords. If companies are willing to pay dozens of dollars per click for certain keywords, they must be profitable.
27. Use the “allintitle” search operator to evaluate keyword competition. Type “allintitle:your keyword” in Google to see the number of website pages optimized for your keyword. Any value above 50,000 will require a serious SEO effort.
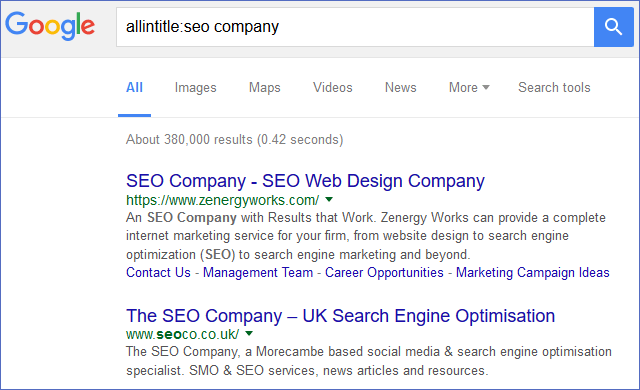
28. Consider both “allintitle” competition and the strength of the top 10 competitors before choosing a keyword.
29. Take user intent into account, targeting buyer keywords with specific prefixes. Most buyer keywords have prefixes like buy, discount, how to, cure, coupon, help for, etc.
30. Optimize for long-tail conversational keywords due to the rise in voice-based searches.
31. Check Google’s first search results page to evaluate the value of targeting a keyword. Organic results may be pushed below the fold by ads, knowledge graphs, and so on, so they may not be worth the effort.
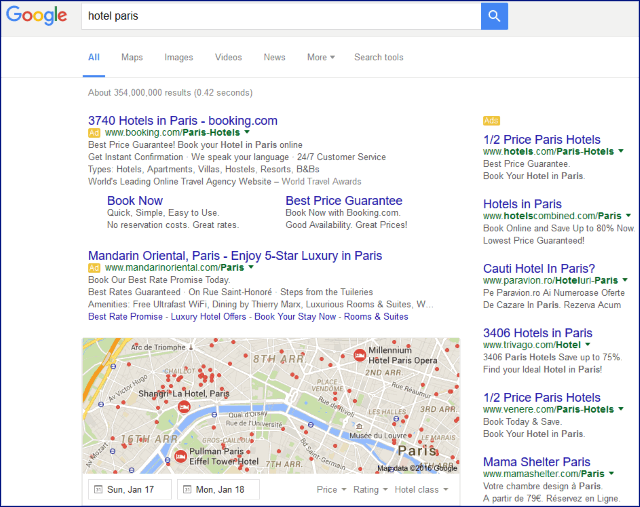
32. Compare multiple data sets from different tools for making keyword decisions.
33. Choose easily rankable keywords, avoiding highly competitive ones unless prepared for a significant investment.
34. Use Link Assistant’s Rank Tracker to monitor keyword rankings across search engines.
35. Daily rankings changes are irrelevant for long-term success. Check keyword positions weekly.
Part 3: Content Tips
36. Use Alltop and reddit for fresh blog post ideas.
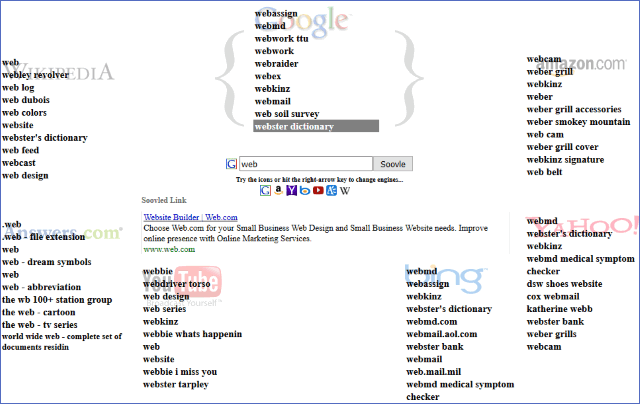
37. Get original article ideas using Wikipedia, Answers.com, YouTube, Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Amazon via Soovle.
38. Set up Google Alerts for industry-related keywords to receive content suggestions.
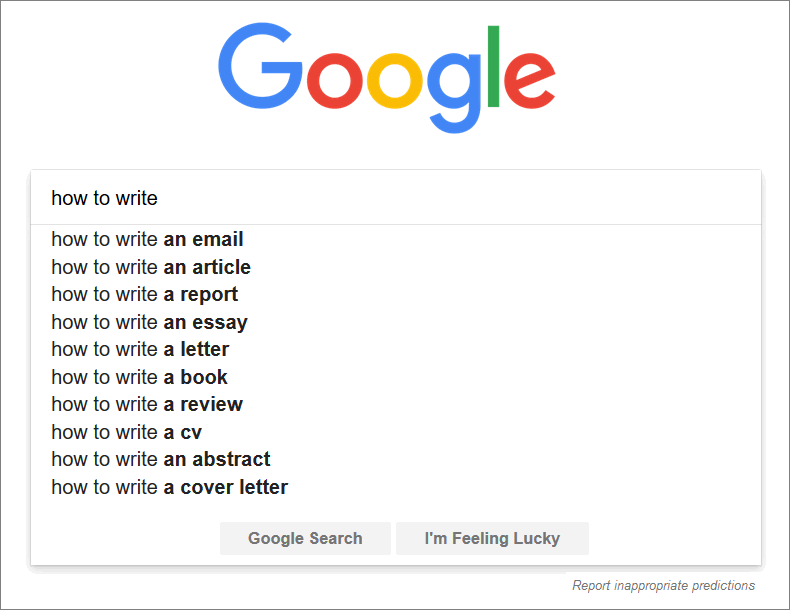
39. Use search query-related questions as subheadings to improve rankings. Google’s autocomplete can help you discover questions that people are asking about your topic.
40. Enhance blog posts with high-quality multimedia to increase engagement. Use great images, infographics, and videos.
41. Regularly update posts to maintain relevance in Google’s rankings. Add new information, update graphs, images, etc.
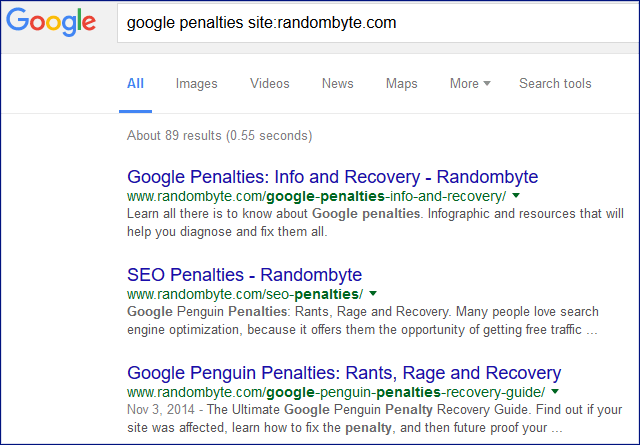
42. Avoid duplicate content by using Google searches to find similar pages. Use Google searches like the one below to reveal pages that may have similar content. Compare articles and remove similar paragraphs.
keyword site:yoursite.com
43. Block access to necessary duplicate pages using robots.txt.

44. Use Copyscape to check for duplicate content and ensure uniqueness.
45. Rewrite product descriptions on e-commerce sites to avoid duplicate content penalties. If you simply copy/paste manufacturers’ descriptions, you’re going to have a hard time trying to rank those product pages.
46. Create content naturally, without obsessing over keyword density.
47. Prioritize well-written, long-form content (1,000+ words) that comprehensively covers a topic.
48. Use Buzzsumo to overcome writer’s block by discovering popular articles.
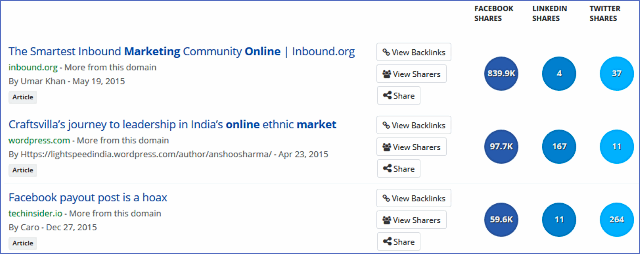
49. Create content that’s better than the articles discovered by Buzzsumo. Then, use a backlinks discovery tool to find out who has linked to those articles. Show the webmasters your much better content and earn high-quality links.
50. Diversify content creation with videos, interviews, contests, etc.
51. Repurpose successful content into different formats and share on various platforms.
52. Target high-value, low-volume keywords for your blog posts.
53. Identify customer problems on Quora and write reports to solve them. Use those reports for lead generation and/or upload them to popular document sharing sites.
54. Avoid spun content; it’s easily identifiable and penalized by Google.
55. Keep content updated and fix broken links using tools like Broken Link Checker.
56. Link out to authoritative industry websites to signal quality to Google.
57. Does your site fall in the YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) category? Ensure site content is accurate and helpful to avoid penalties.
58. Use Google Search Console to index new blog posts quickly: “Crawl” -> “Fetch as Google”.
Part 4: On-page SEO Tips
59. Make paid and affiliate links nofollow to comply with Google’s guidelines.
<a href=”https://www.yoursite.com/your-affiliate-url” rel=”nofollow”>This is an affiliate link</a>
60. Combine similar low-quality pages into one high-quality page to avoid Panda penalties.
61. Use Flickr’s advanced search for royalty-free blog post images.
62. Optimize image filenames, titles, and alt tags using your targeted keywords.
63. Avoid embedding text in images; Google prefers plain text and rewards it accordingly.
64. Keep title tags within 50-60 characters for optimal display in Google search results.
65. Create unique description tags, limiting them to 150 characters and turning them into strong calls-to-action.
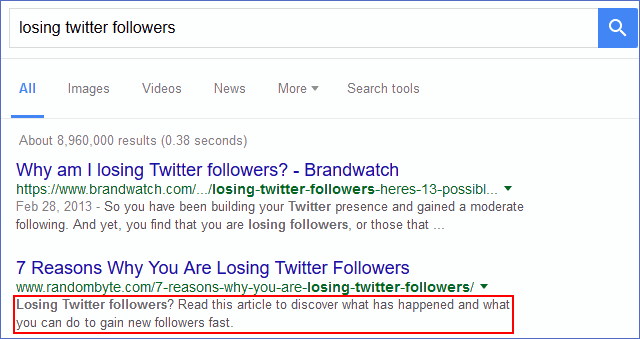
66. Redirect dynamic URLs to their static equivalents.
67. Fix 404 errors promptly using tools like Search Console or Screaming Frog SEO Spider.
68. Add structured data markup and test it using Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool.
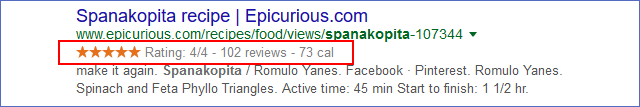
Websites that use microdata have higher click-through rates, attracting more visitors.
69. Optimize content to appear as featured snippets and in the ‘People also ask’ section by analyzing existing results and improving upon them.
70. Focus on acquiring high-quality links after optimizing on-page SEO.
Part 5: User Experience Tips
71. Google evaluates relevance, content quality, compatibility, and loading speed. Engaging content leads to higher search engine rankings.
72. Avoid tabbed content and infinite scrolling as they might hinder search engine readability.
73. Optimize pop-ups for user experience; avoid large pop-ups on small screens to prevent penalties.
74. Use Crazy Egg to analyze and optimize user interactions on your site.
75. Invest in high-quality images for articles to attract visitors and improve engagement.
76. Use interactive content to keep visitors returning and engaged, which search engines reward.
77. Monitor and improve click-through rates using Google Search Console to ensure effective titles and descriptions.
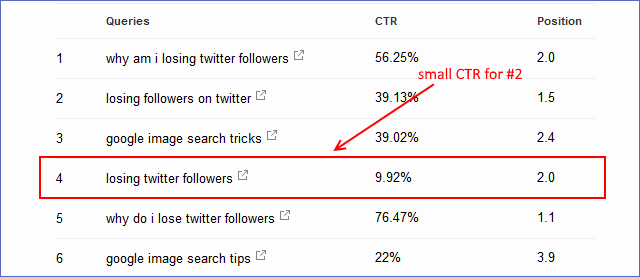
78. Study successful ad titles and descriptions for inspiration and effectiveness.
79. Lower website bounce rates to improve dwell time and user engagement. Low dwell times indicate that your content may not be engaging or interesting to visitors.
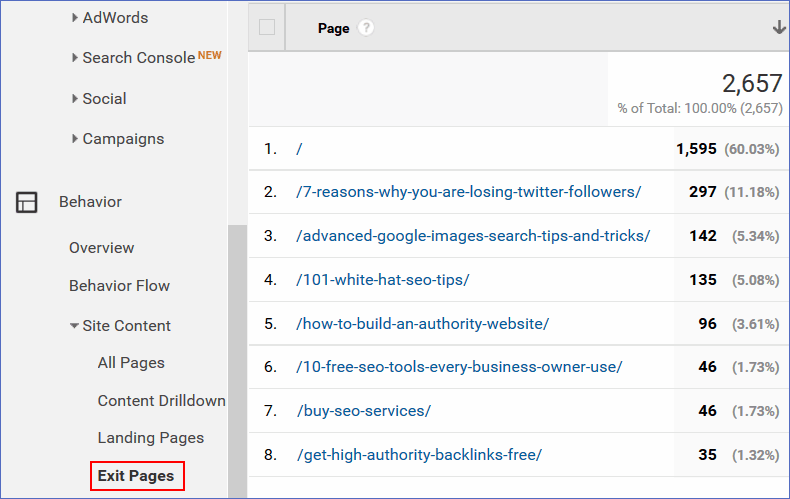
80. Use analytics to identify and improve exit pages, increasing the time visitors spend on your site.
Part 6: Off-page SEO / Link Building Tips
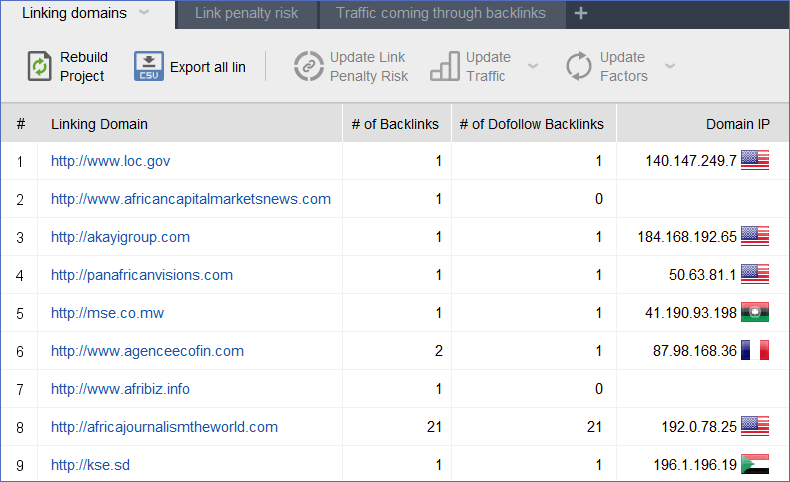
81. Use SEO Spyglass to discover and replicate competitors’ best backlinks.
82. Combine Google’s advanced search operators for unique link opportunities. Use industry slang and “intitle”, “inurl”, “intext” to create your custom search strings.
83. Use synonyms and related words in search queries for guest blogging opportunities. Many people try to find guest blogging opportunities by typing their keyword + “write for us” into Google’s search box, but few search for their keyword + “write for me”.
84. Explore advanced search operators for Yahoo, Bing, etc., for uncommon link building opportunities.
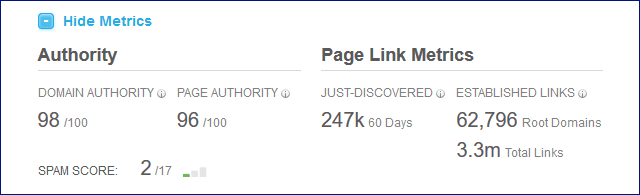
85. Evaluate a site’s SEO power using Majestic SEO’s Citation Flow/Trust Flow and Moz’s Domain Authority/Page Authority.
86. Choose contextual links over sitewide links; they deliver much better SEO value.
87. Avoid reciprocal link building; instead, focus on earning high-quality backlinks. Google is familiar with three way linking schemes as well, so avoid them.
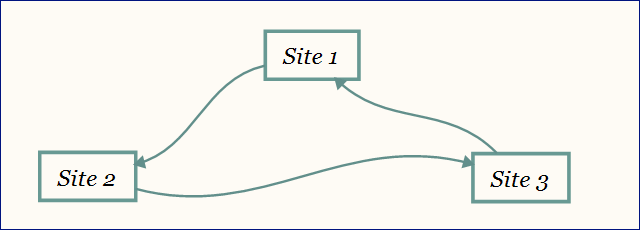
88. Use press releases strategically for authentic news. Don’t use them for SEO purposes – they will only provide a temporary boost for low competition keywords.
89. Keep link request emails short and offer value in exchange for links.
90. Target valuable links that send both authority and targeted traffic.
91. Set up Google Alerts to turn unlinked website mentions into backlinks.
92. Use brand and URL-based anchor texts to avoid over-optimization.
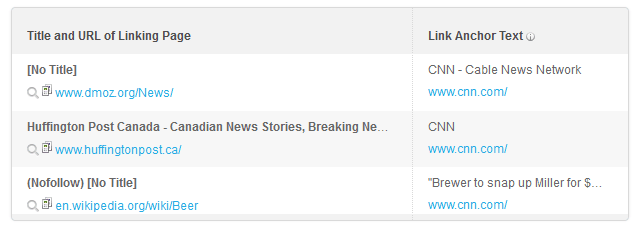
93. Get nofollow links as well; they help maintain a natural backlink profile.
94. Create infographics with tools like infogr.am or Piktochart for effective link building.
95. Use tools like Broken Link Checker for broken link building. Learn more about this link building technique by reading my article: The A to Z Broken Link Building Guide for Evergreen SEO Success.
96. Focus on acquiring a few high-quality links rather than many low-quality ones.
97. Add your site to authoritative business directories. Here are some ways of getting high authority backlinks for free.
98. Diversify your link sources to make your SEO strategy harder to replicate.
99. Use Google Alerts to find new industry websites open to guest posts.
100. Monitor new competitors breaking into the top 20 to discover fresh, effective SEO techniques.
Part 7: Website Traffic Tips
101. Explore diverse traffic sources besides SEO, such as forums, ethical article marketing, guest posting, offline marketing (flyers, etc), Q & A sites, document sharing sites and giveaways.
102. Focus on low-volume, high-conversion keywords to boost sales.
103. Use Google’s Search Console to uncover “not provided” keywords.
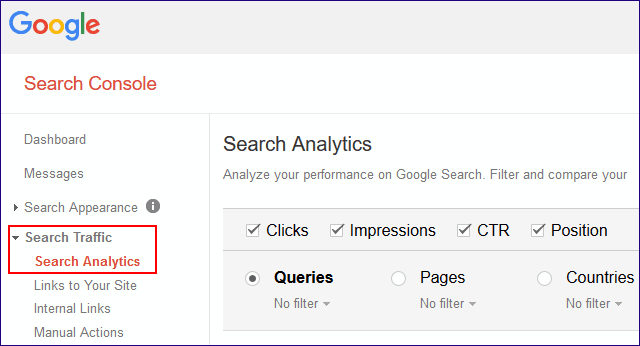
104. Set up Google Analytics alerts for sudden traffic drops with Intelligence Events -> Create a Custom Alert.
Part 8: SEO Tools
105. Use Google Analytics for comprehensive site performance tracking, or StatCounter as an alternative.
106. Use SEMrush, Spyfu, or Ahrefs to identify second-page keywords and boost them with internal links.
107. Don’t want to pay for a backlinks discovery tool? Use Open Link Profiler.
108. Monitor website downtime with UptimeRobot; you will be notified by email and/or SMS whenever your website is down.
109. Identify potential partners and competitors with SimilarSites and SimilarWeb.
110. Discover industry questions and content ideas using FAQ Fox.
111. Use Google Public Data for creating insightful data-driven content.
112. Generate catchy article titles with Portent’s Content Idea Generator.

113. Design attractive images with Canva, even without graphic design skills.

114. Use Bulk DA Checker to assess domain authority metrics.
115. Earn backlinks from reputable news sites by registering with Connectively.
116. Verify email addresses with MailTester.com before outreach to avoid spam flags.
117. Use a comprehensive SEO questionnaire for new clients. Here’s one of the best SEO questionnaires I could find.
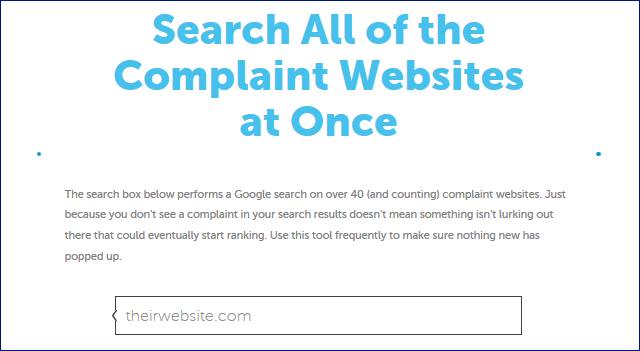
118. Monitor your online reputation using the Complaints Search Results engine.
119. Use https://www.webpagetest.org/ to speed up your site and boost its SEO rankings.
120. Regularly audit your site with tools like Website Auditor for problem areas.
Part 9: Social Media Tips
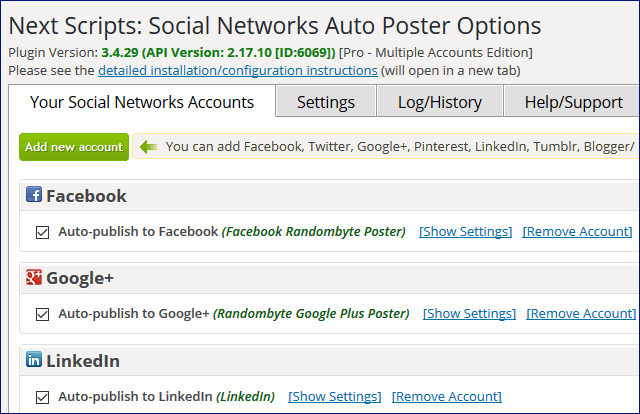
121. Create consistent social media profiles on LinkedIn, Instagram, etc. Then, use tools like Social Networks Auto-Poster to share content automatically.
122. Email links to your new blog posts to subscribers and share them in relevant forums.
123. Add social sharing buttons to blog posts for easy sharing.

124. Include long-tail keywords in social media profiles. Those domains have a high authority, so they may rank on Google’s first page for your keywords on their own.
125. Share varied content, including others’ articles, to build authority.
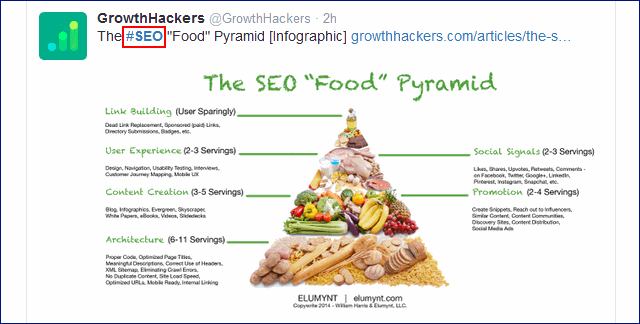
126. Use relevant hashtags in all posts to increase visibility.
127. Brand all visual content and share it on social media for more traffic.
128. Request shares for outstanding content, not just average posts.
129. Measure performance by tracking real followers and engagement. Don’t ever buy followers, views, etc.
130. Post updates when they are most likely to be noticed and shared. Here are the best times to post on social media.
Part 10: WordPress SEO Tips
131. Use an SEO-optimized theme for better site performance and rankings.
132. Ensure each page has a single <h1> tag assigned to the page/post title.
133. Submit your RSS feed URL to the top directories to get links and visitors on autopilot every time you post a fresh article.
134. Optimize your sidebar to prevent navigation issues and slowdowns.
135. Install the Google XML Sitemaps plugin for efficient site indexing.
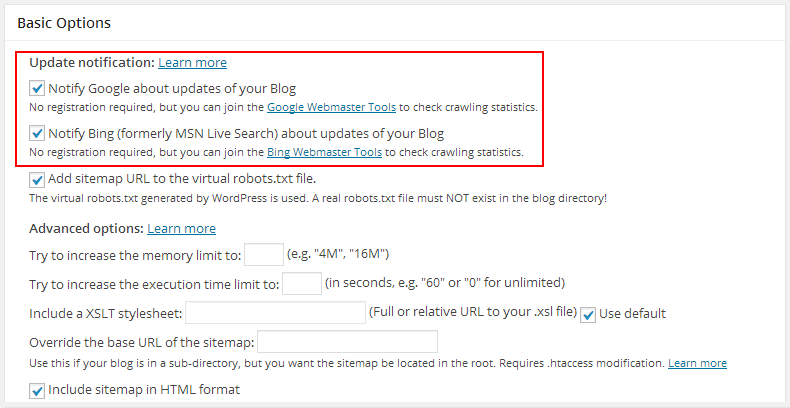
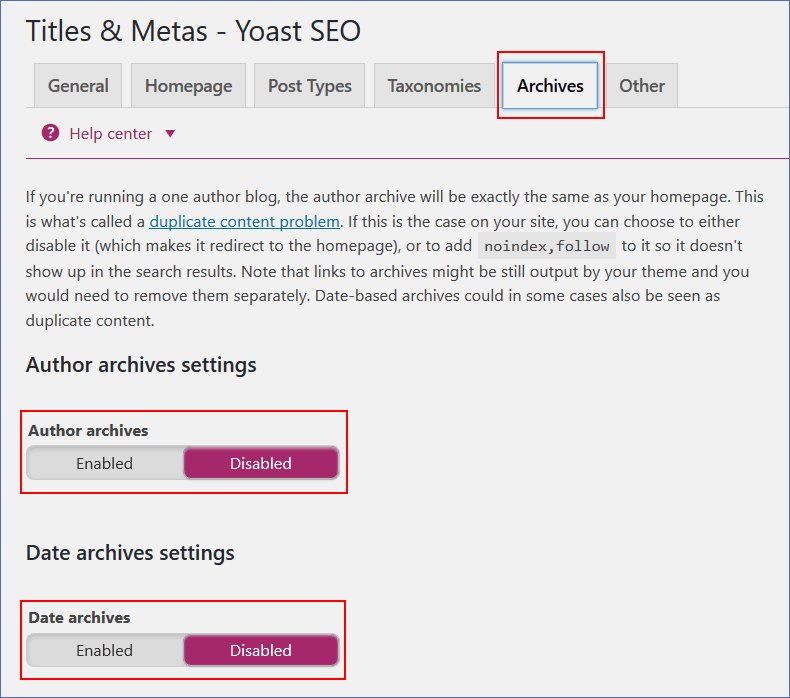
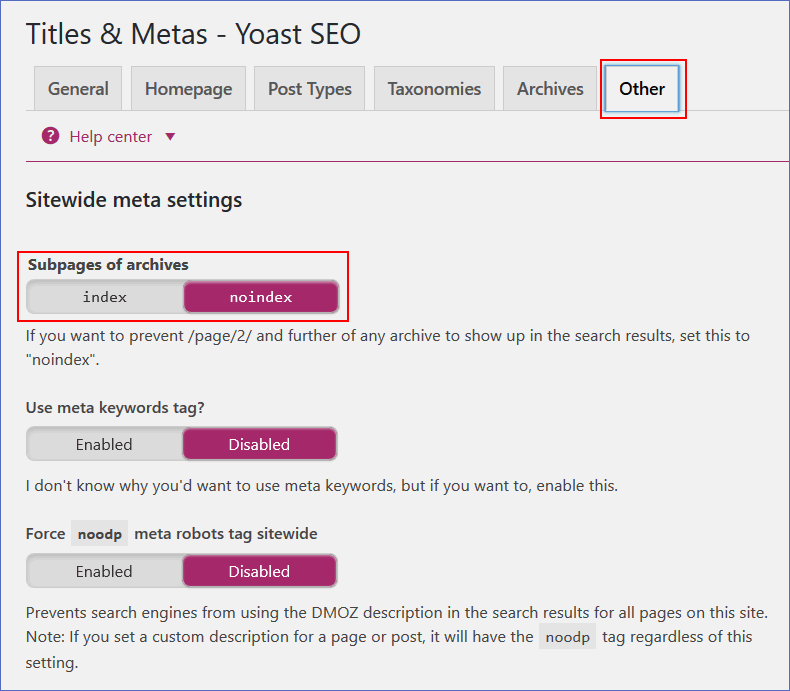
136. Configure the Yoast SEO plugin and disable unnecessary archives:
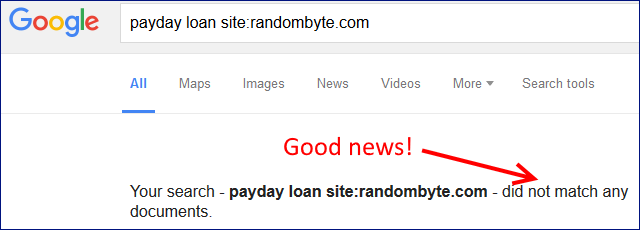
– Author archives, for single-author blogs;
– Date archives, if you aren’t using them;
– Subpages of archives.
137. Use a caching plugin like W3 Total Cache to improve loading speeds.
138. Regularly back up your site with plugins like BackUpWordPress.
139. Automatically nofollow affiliate links with Pretty Links to avoid penalties.
140. Use schema markup plugins if your theme lacks built-in support.
141. Implement a related posts feature to boost site engagement. Jetpack is installed by default with WordPress, and it includes a related posts feature as well. Other popular plug-ins are YARPP and Contextual Related Posts.
142. Identify and replace slow plugins using Query Monitor.
143. Explore the most popular plugins in the WordPress Plug-ins Directory; some of them are useful. Check the number of active installations, ratings, etc.
144. Use rel=”canonical” to handle pages assigned to multiple categories.
145. Use a top-rated managed WordPress hosting package, or at least a company that offers WordPress-friendly hosting accounts.
Part 11: Google Penalties and Recovery
146. Regularly audit your backlink profile and disavow harmful links.
147. Monitor for manual penalty messages in Google Search Console.

148. Improve or remove low-quality content to avoid Panda penalties.
149. Avoid automated link-building tools; they may trigger Penguin penalties. Forum profile links, directory links, blog comments links and keyword-rich links are known Penguin triggers.
150. Maintain a clean site with up-to-date CMS and plugins. Back up the site at least once a week; this service may be included in your hosting package for free.
151. Moderate user-generated content to prevent linking to bad sites.
152. Read my Google Penalties: Info and Recovery article.
Part 12: General SEO Tips and Advice
153. Skip website submission services; instead, use social media accounts that point to your site for quick indexing.
154. Forums attract visitors, boosting site authority and building your brand. Create a forum if you can dedicate time to moderate and engage users.
155. Use Copyscape to monitor for copied content. Contact the offenders and ask them to remove your content from their sites. If they don’t comply, report their websites to Google.
If people copy and use your articles regularly, consider subscribing to the $10 / month DMCA Website Protection Pro service.
156. If you run a local business, ensure consistent NAP (name, address, phone number) information across all platforms for local SEO.
157. Set up Google Alerts to study relevant sites’ success strategies.
158. Invest in reliable hosting to avoid ranking drops due to downtime.
159. Avoid sharing IP addresses with spammers on shared hosting plans. Sites like this will compare your site’s IP address with known, spammy IPs.
160. Use a CDN like Cloudflare for faster site delivery.
161. Ensure your site properly redirects non-www to www URLs (or vice versa) using 301 redirects.
162. Check for invisible malicious links using keyword site searches.
A sudden ranking/ website traffic drop is either the result of a major search engine algorithm update or indicates that your website has been hacked.
163. Revive pages in Google’s supplemental index by enhancing their content and building high-quality links to them.
164. Optimize your site for mobile devices using responsive design.
165. Prioritize top-performing pages to maximize conversions. Write more content to support those pages, and build links to them.
166. Secure your site with HTTPS, ensuring all elements use secure links.
167. Adopt white hat SEO strategies for sustainable, long-term traffic growth. Remember that Google has incorporated delays into its algorithm, because it wants to prevent SEOs from manipulating search results.
Further reading: